Use Flux in Chronograf dashboards
This page documents an earlier version of InfluxDB OSS. InfluxDB 3 Core is the latest stable version.
Chronograf is the web user interface for managing for the InfluxData platform that lest you create and customize dashboards that visualize your data. Visualized data is retrieved using either an InfluxQL or Flux query. This guide walks through using Flux queries in Chronograf dashboard cells.
Using Flux in dashboard cells
Chronograf v1.8+ and InfluxDB v1.8+ with Flux enabled are required for Flux in dashboards.
To use Flux in a dashboard cell, either create a new cell or edit an existing cell by clicking the pencil icon in the top right corner of the cell. To the right of the Source dropdown above the graph preview, select Flux as the source type.

The Flux source type is only available if your data source has Flux enabled.
This will provide Schema, Script, and Functions panes.
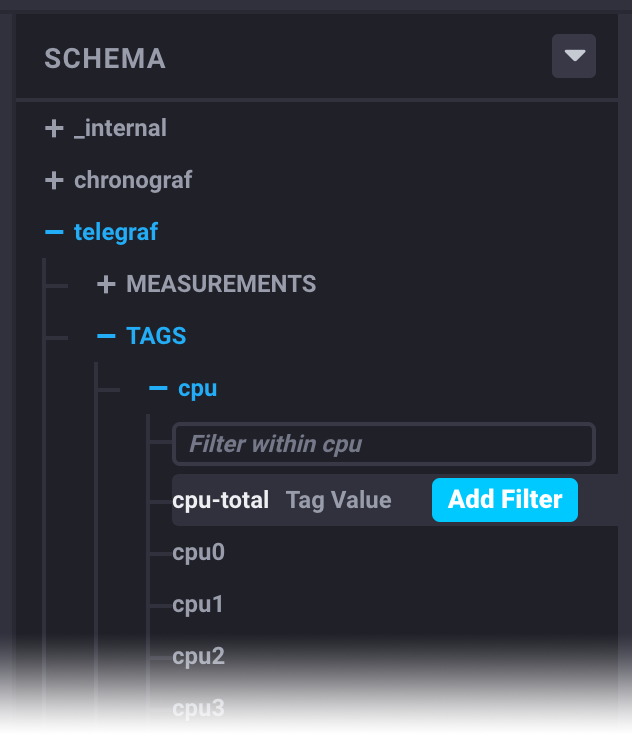
Schema pane
The Schema pane allows you to explore your data and add filters for specific measurements, fields, and tags to your Flux script.
Script pane
The Script pane is where you write your Flux script. In its default state, the Script pane includes an optional Script Wizard that uses selected options to build a Flux query for you. The generated query includes all the relevant functions and template variables required to return your desired data.
Functions pane
The Functions pane provides a list of functions available in your Flux queries. Clicking on a function will add it to the end of the script in the Script pane. Hovering over a function provides documentation for the function as well as links to deep documentation.
Dynamic sources
Chronograf can be configured with multiple data sources. The Sources dropdown allows you to select a specific data source to connect to, but a Dynamic Source options is also available. With a dynamic source, the cell will query data from whatever data source to which Chronograf is currently connected. Connections are managed under Chronograf’s Configuration tab.
View raw data
As you’re building your Flux scripts, each function processes or transforms your data is ways specific to the function. It can be helpful to view the actual data in order to see how it is being shaped. The View Raw Data toggle above the data visualization switches between graphed data and raw data shown in table form.
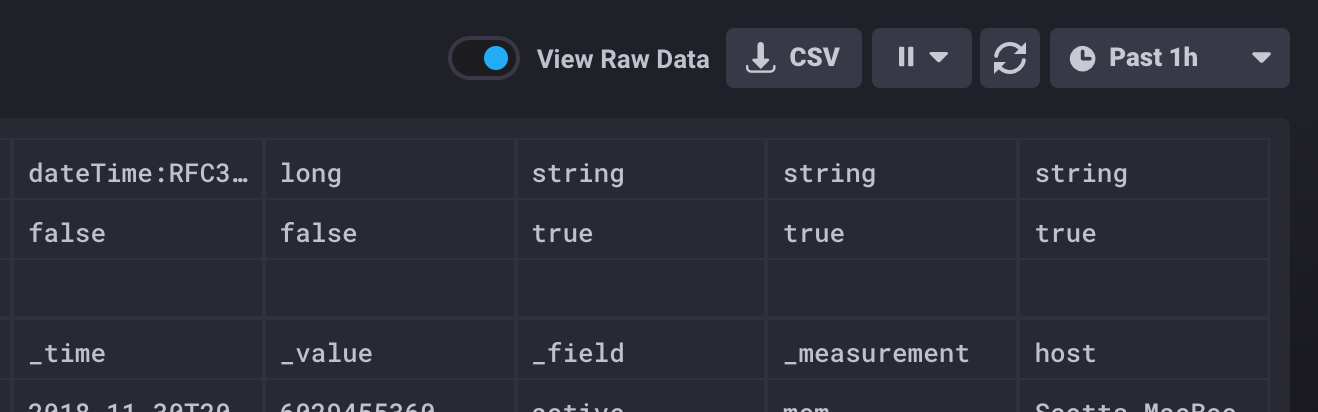
The View Raw Data toggle is only available when using Flux.
Template variables in Flux
Chronograf template variables allow you to alter specific components of cells’ queries using elements provided in the Chronograf user interface.
In your Flux query, reference template variables just as you would reference defined Flux variables.
The following example uses Chronograf’s predefined template variables,
dashboardTime, upperDashboardTime, and autoInterval:
from(bucket: "telegraf/autogen")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r._measurement == "cpu")
|> range(
start: dashboardTime,
stop: upperDashboardTime
)
window(every: autoInterval)Predefined template variables
dashboardTime
The dashboardTime template variable represents the lower time bound of ranged data.
It’s value is controlled by the time dropdown in your dashboard.
It should be used to define the start parameter of the range() function.
dataSet
|> range(
start: dashboardTime
)upperDashboardTime
The upperDashboardTime template variable represents the upper time bound of ranged data.
It’s value is modified by the time dropdown in your dashboard when using an absolute time range.
It should be used to define the stop parameter of the range() function.
dataSet
|> range(
start: dashboardTime,
stop: upperDashboardTime
)As a best practice, always set the
stopparameter of therange()function toupperDashboardTimein cell queries. Without it,stopdefaults to “now” and the absolute upper range bound selected in the time dropdown is not honored, potentially causing unnecessary load on InfluxDB.
autoInterval
The autoInterval template variable represents the refresh interval of the dashboard
and is controlled by the refresh interval dropdown.
It’s typically used to align window intervals created in
windowing and aggregation operations with dashboard refreshes.
dataSet
|> range(
start: dashboardTime,
stop: upperDashboardTime
)
|> aggregateWindow(
every: autoInterval,
fn: mean
)Custom template variables
<% warn %> Chronograf does not support the use of custom template variables in Flux queries. <% /warn %>
Using Flux and InfluxQL
Within individual dashboard cells, the use of Flux and InfluxQL is mutually exclusive. However, a dashboard may consist of different cells, each using Flux or InfluxQL.
Was this page helpful?
Thank you for your feedback!
Support and feedback
Thank you for being part of our community! We welcome and encourage your feedback and bug reports for InfluxDB and this documentation. To find support, use the following resources:
Customers with an annual or support contract can contact InfluxData Support.
